Deep Foundation: Placement, Installation, and Repetition of Piles
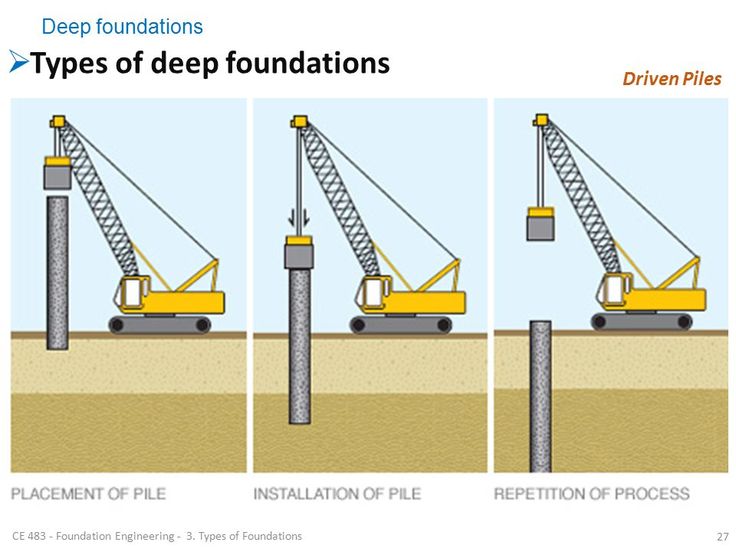
Deep foundations play a crucial role in supporting structures that require stability on weak or unstable soils. Unlike shallow foundations, which transfer loads near the surface, deep foundations reach into stronger soil or rock layers to provide the necessary support. Among the various types of deep foundations, piles are one of the most commonly used elements in construction. Piles are long, slender columns made of materials such as concrete, steel, or timber, driven deep into the ground to support heavy structures.
This article will explore the placement, installation, and repetition of piles in deep foundation construction. Understanding these processes is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and longevity of buildings, bridges, and other infrastructure projects that rely on pile foundations.
1. Placement of Piles
The placement of piles refers to the strategic positioning of these structural elements to effectively transfer loads from a building or structure to deeper, more stable soil layers or bedrock. The proper placement of piles is critical for maintaining the foundation’s strength, stability, and resistance to settlement.
Factors Affecting Pile Placement
Several factors influence the placement of piles in a construction project, including:
- Soil Conditions: The type and strength of the soil determine where piles should be positioned for maximum stability.
- Load Distribution: Piles must be arranged to distribute loads evenly and prevent structural failure.
- Spacing Requirements: Proper spacing ensures that adjacent piles do not interfere with each other or cause excessive soil displacement.
- Environmental Constraints: Considerations such as underground utilities, water bodies, and existing structures affect pile placement.
Pile Layout Planning
Before piles are placed, engineers develop a detailed pile layout plan using geotechnical surveys, soil tests, and structural load calculations. The layout is designed to ensure that each pile effectively transfers loads and minimizes the risk of settlement or tilting.
Marking Pile Locations
Once the plan is finalized, pile locations are marked on-site using surveying techniques such as GPS mapping, total stations, and chalk lines. These markers guide construction workers and heavy machinery during the pile installation process.
2. Installation of Piles
The installation of piles involves driving or drilling piles into the ground using specialized equipment. This process requires precision and expertise to ensure that each pile reaches the desired depth and maintains its structural integrity.
Methods of Pile Installation
There are several methods used to install piles, depending on the type of pile and soil conditions:
-
Driven Piles
- These piles are hammered into the ground using a pile driver, which may be hydraulic, diesel, or vibratory.
- Common materials for driven piles include steel, concrete, and timber.
- This method is effective in dense soils but may cause noise and vibrations that can affect nearby structures.
-
Bored Piles (Drilled Shafts)
- In this method, a hole is drilled into the ground before a reinforced concrete pile is cast in place.
- Bored piles are suitable for areas where noise and vibration must be minimized.
- They provide high load-bearing capacity, making them ideal for bridges and skyscrapers.
-
Screw Piles (Helical Piles)
- These piles are rotated into the ground like screws using specialized machinery.
- Helical piles are commonly used for lightweight structures and temporary foundations.
- They are quick to install and do not require curing time like concrete piles.
-
Micro Piles
- Small-diameter piles that are drilled and reinforced with steel bars.
- Used in restricted spaces or for reinforcing existing foundations.
Installation Process
Regardless of the method used, the installation of piles follows a series of steps:
- Site Preparation: Clear the area of obstacles and ensure the ground is stable.
- Pile Positioning: Align the pile with the marked placement locations.
- Driving or Drilling: Use the chosen installation method to embed the pile into the ground.
- Quality Control: Conduct load tests and inspections to ensure each pile meets structural requirements.
3. Repetition of Piles
The repetition of piles refers to the systematic and repetitive process of installing multiple piles across a construction site to support large structures. Since deep foundations often require numerous piles, their installation must be carried out efficiently and consistently.
Importance of Pile Repetition
- Uniform Load Distribution: A repetitive arrangement of piles ensures even weight distribution across the foundation.
- Structural Stability: Consistent pile installation prevents differential settlement and uneven stress points.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Standardized procedures for pile repetition speed up the construction process and reduce costs.
Techniques for Efficient Pile Repetition
- Batch Installation: Piles are installed in groups or sections to maintain efficiency and workflow continuity.
- Automated Equipment: Advanced machinery allows for faster and more precise repetition of pile installation.
- Prefabrication: Some piles, such as precast concrete piles, can be manufactured off-site and installed rapidly in sequence.
- Monitoring and Adjustments: Engineers continuously monitor the installation process to detect any deviations and make necessary corrections.
Challenges in Repetition of Piles
- Soil Variability: Changes in soil conditions may require adjustments in pile depth or installation technique.
- Obstructions: Underground obstacles like rocks or old foundations can delay the repetitive piling process.
- Weather Conditions: Rain, wind, and temperature fluctuations may impact pile installation timelines.
Conclusion
The construction of deep foundations using piles is a highly technical and methodical process that requires careful planning, precision, and expertise. The placement of piles ensures that they are positioned correctly to support structural loads, while the installation of piles involves various techniques such as driving, drilling, or screwing them into the ground. Finally, the repetition of piles allows for the systematic and efficient installation of multiple piles across a foundation to maintain stability and strength.
By following best practices in pile placement, installation, and repetition, engineers and construction professionals can build durable, long-lasting foundations for buildings, bridges, and other critical infrastructure projects.
