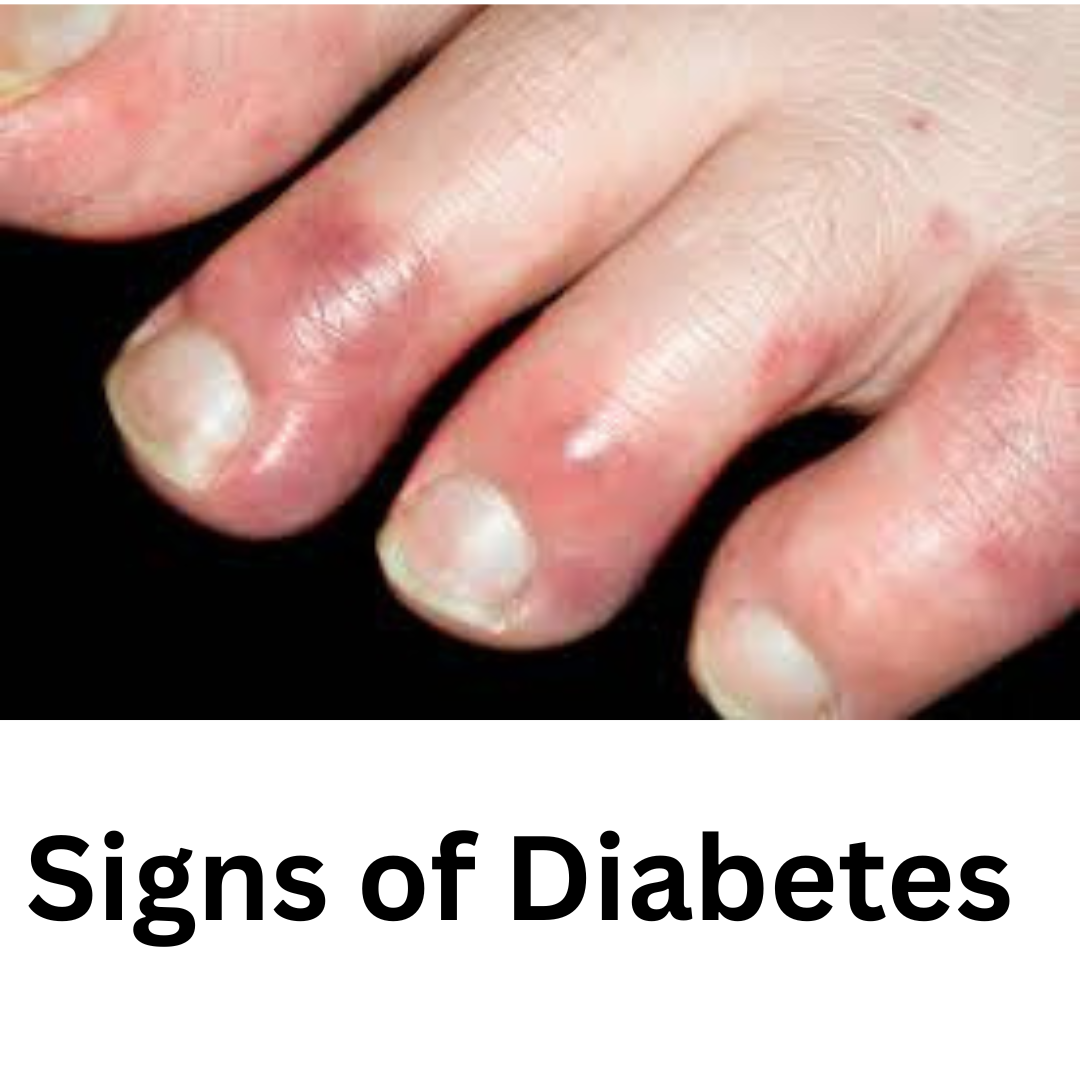
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that impairs the body’s ability to process glucose, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. There are two main types: Type 1, an autoimmune condition usually diagnosed in childhood, and Type 2, often related to lifestyle factors and more common in adults. Early symptoms of diabetes include excessive thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow wound healing. If these signs are ignored, diabetes can cause long-term complications such as nerve damage, vision loss, kidney failure, and cardiovascular disease.
Diagnosis is done through blood tests like the fasting glucose test or HbA1c test. Managing diabetes involves monitoring blood sugar levels, adopting a balanced diet, staying active, and possibly using medication or insulin therapy. Early detection and proactive management are key to preventing complications and maintaining quality of life. Anyone experiencing early symptoms should consult a healthcare provider for screening and guidance.