Red dots on the skin are a surprisingly common phenomenon that most people experience at some point in their lives. These small, often painless spots can appear suddenly or gradually and may vary in size, color, and cause. While some red dots are harmless and resolve on their own, others may signal a deeper health issue that needs attention. Understanding the different causes and types of red dots on the skin is essential for determining when to seek medical advice and how to manage them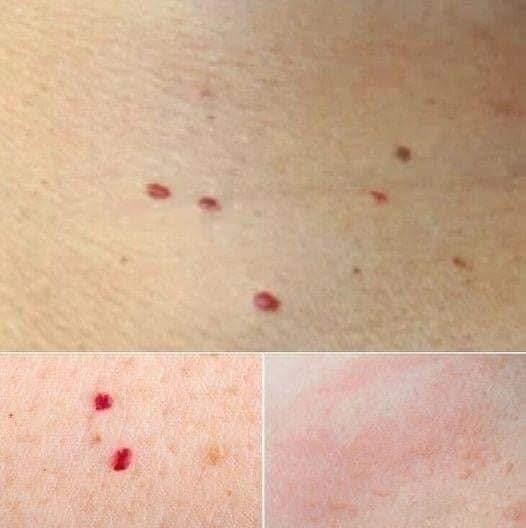 .
.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the top ten causes of red dots on the skin, explore the potential health implications, and provide helpful tips for prevention and treatment.
1. Petechiae and Purpura: Tiny Red Dots from Damaged Blood Vessels
Petechiae are tiny, pinpoint red or purple dots that appear under the skin due to minor bleeding from broken capillaries. They do not fade when you press on them, which helps distinguish them from a simple rash. Petechiae can result from physical stress (such as intense coughing or vomiting), certain medications, infections, or platelet disorders. When petechiae occur in clusters or alongside other symptoms like fever or fatigue, they may indicate a serious condition such as a blood clotting disorder or infection like meningitis. Purpura is a similar but larger form of bleeding under the skin.
If you notice petechiae or purpura with other concerning symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation to rule out underlying conditions.
2. Cherry Angiomas: Harmless Red Bumps
Cherry angiomas are small, round, bright red growths made up of blood vessels. They are incredibly common, especially in people over 30, and are typically benign. These dots can appear anywhere on the body but are most often found on the torso, arms, and shoulders. The exact cause of cherry angiomas is unknown, but they tend to increase in number with age and may have a genetic component.
While cherry angiomas don’t usually require treatment, some people choose to remove them for cosmetic reasons. Treatments include laser therapy, cryotherapy (freezing), or electrosurgery.
3. Heat Rash: Skin Irritation from Trapped Sweat
Heat rash, also known as miliaria, develops when sweat becomes trapped in sweat ducts beneath the skin. This condition is especially common in hot, humid environments or after intense physical activity. It typically presents as red or pink dots or blisters, often accompanied by itching or a prickling sensation.
Heat rash is most common in babies but can affect people of all ages. Keeping the skin cool and dry, wearing loose clothing, and avoiding overheating can help prevent and treat heat rash. Most cases resolve on their own without medical treatment.
4. Allergic Reactions: Redness from Body’s Immune Response
Red dots can also result from allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect stings, or contact with allergens like latex or certain plants. These reactions often manifest as hives or a widespread rash with red, itchy welts or dots.
In some cases, allergic reactions can escalate into anaphylaxis, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. If red dots appear suddenly, especially after eating or taking a new medication, and are accompanied by swelling or difficulty breathing, seek emergency care.
5. Folliculitis: Inflamed Hair Follicles
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of the hair follicles that can cause small, red, pimple-like bumps. These may be filled with pus and can appear anywhere hair grows, including the scalp, legs, arms, or buttocks. Causes include bacterial or fungal infections, irritation from shaving, or blockage from oils and lotions.
Mild folliculitis usually resolves on its own with good hygiene and warm compresses. More persistent or severe cases may require topical or oral antibiotics or antifungal medications.
6. Cellulitis: A Serious Skin Infection
Unlike harmless skin issues, cellulitis is a bacterial infection that penetrates deeper layers of the skin. It typically appears as a red, swollen area that is warm to the touch and may spread rapidly. Although red dots may not be the first sign, they can accompany the swelling and indicate underlying infection.
Cellulitis requires prompt medical treatment with antibiotics to prevent the infection from spreading to the bloodstream, which can become life-threatening.
7. Impetigo: Highly Contagious Red Sores
Impetigo is a common and contagious skin infection that primarily affects children but can also occur in adults. It begins with red sores or blisters that may ooze fluid and develop a yellow-brown crust. Caused by Staphylococcus or Streptococcus bacteria, impetigo spreads easily through direct contact.
Treatment includes prescription antibiotic ointments or oral antibiotics. Preventing spread involves good hygiene, avoiding scratching, and not sharing towels or personal items.
8. Vasculitis: Inflammation of Blood Vessels
Vasculitis refers to inflammation of the blood vessels, which can affect their function and lead to red or purple spots on the skin. These dots are usually the result of bleeding beneath the surface due to the vessel damage. Vasculitis can be triggered by infections, autoimmune diseases, or medications and can affect organs throughout the body.
Symptoms can vary widely and may include fatigue, joint pain, and fever, along with the appearance of red dots or rashes. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve corticosteroids or immunosuppressive medications.
9. Hemangiomas: Benign Blood Vessel Growths
Hemangiomas are birthmarks or growths made up of an abnormal collection of blood vessels. They often appear shortly after birth and may look like raised red dots or bumps on the skin. Most hemangiomas are harmless and fade over time without treatment.
However, if a hemangioma interferes with vision, breathing, or feeding (depending on its location), or grows rapidly, medical evaluation and treatment may be necessary. Treatments include beta-blocker medications or laser therapy in rare cases.
10. When to Worry: Red Dots That Require Medical Attention
While many red dots are benign and self-resolving, certain signs should prompt a visit to a healthcare provider. These include:
- Sudden appearance of red dots with no clear cause
- Accompanying symptoms like fever, fatigue, or swelling
- Red dots that don’t fade when pressed (suggestive of petechiae)
- Painful, spreading, or pus-filled lesions
- Dots associated with difficulty breathing or allergic reaction
Early diagnosis can be crucial, especially if the red dots are part of a systemic illness or infection.
Preventive Measures and Skin Care Tips
Maintaining healthy skin is key to preventing many causes of red dots. Consider these tips:
- Practice good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items
- Use gentle, non-irritating skin products
- Wear breathable fabrics in hot weather to prevent heat rash
- Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins A, C, and E
- Avoid known allergens and use sunscreen to protect against sun damage
Final Thoughts
Red dots on the skin can be alarming, but understanding their possible causes can help you respond appropriately. Whether it’s a minor irritation or a sign of something more serious, paying attention to your skin’s signals is a smart move for your overall health. When in doubt, don’t hesitate to consult a medical professional—because when it comes to your skin, it’s always better to be safe than sorry.

